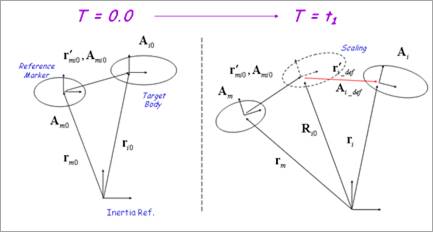
In generally, the system component has a different scale magnitude for a displacement. For example, each component of total assembled car moving the straight road of 10m has a small relative displacement. The displacement of suspension component relative to the attached tire is very small rather than the global motion. Sometimes, it becomes one of the main reasons of simulation that observing such a small displacement. But this observation is not easy to capture. So, RecurDyn supports the Animation Scaling function to enlarge the relatively small displacement. The below figure shows a concept of scaling.


The user can assume that difference between the original position and current position of target body measured from the reference marker is a relative deformation. The user can get the relative deformation with respect to the reference frame as follows
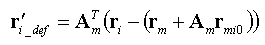
The user should enlarge this relative deformation with some scaling factors. And then the user can easily observe the tendency of target body among the large global motion.
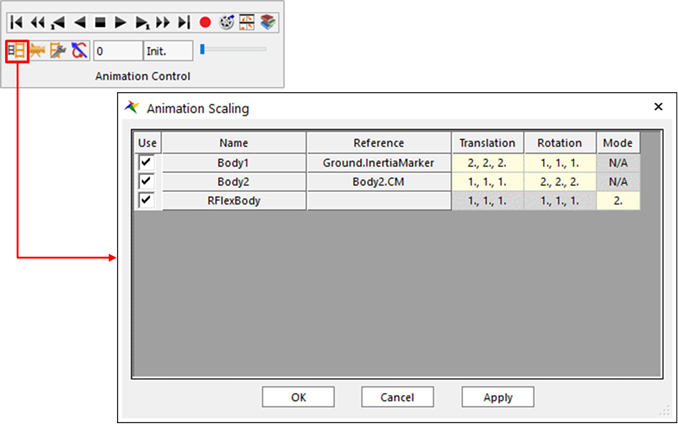
Figure 1 Animation Scaling dialog box
The user can use a way to set the animation scaling option and the user can use two ways to modify the animation scaling option.
To activate the Animation Scaling function, the user must check on the check box at the Graphic Property tab in the Properties of Body dialog box.
It is a little different by types of bodies.
•Rigid Body: is set the relative displacement by some scaling factors with respect to the reference marker. For see more information, refer to Step to create animation scaling.
•FFlex Body: is set the relative deformation by some scaling factors with respect to the reference node. For see more information, refer to Step to create animation scaling.
•RFlex Body: is set the relative deformation by some scaling factors and a mode factor with respect to the reference marker. For see more information, refer to Step to create animation scaling.