1. Select the Monte-Carlo icon of the Reliability group in the AutoDesign tab.

Figure 1 Monte-Carlo icon of the Reliability group in the AutoDesign tab
2. Define the information of random constant
Check ‘Design Variable’ in the ‘Reliability: Monte-Carlo’ dialog and select the probability distribution and deviation value type. The current values of the selected variables are regarded as mean values. As the selected design parameters (DP) are random constants, their types are represented as ‘Constant’.
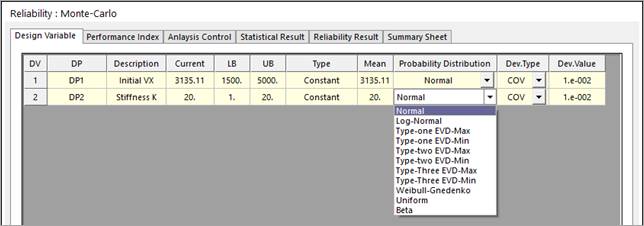
Figure 2 Define the information of random constants
•Probability Distribution: For reliability analysis, one should define the probability distribution type for each random constant. AutoDesign provides 11 types of probability distributions. The detailed information of the probability distributions is explained in Probability Distribution.
•Deviation type: The standard deviation types. SD is ‘standard deviation value’. COV is ‘coefficient of variance’, which is ‘SD/Mean’ value.
3. Define the limit state function
Check ‘Performance Index’ in the ‘Reliability: Monte-Carlo’ dialog and select the analysis responses to define the limit state relation. Figure 3 shows that two ARs are less than their limits. This represents that the system is failed when one of ARs is greater than its’ limit.
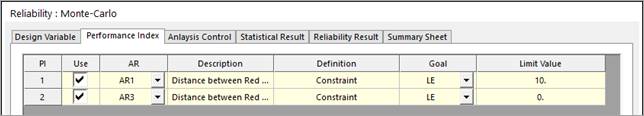
Figure 3 Define the limit state function
4. Define the Analysis Control
Check ‘Analysis Control’ in the ‘Reliability: Monte-Carlo’ dialog. Then, you can see the simple menu window. Define the number of sampling points. The Reliability Analysis explains the guideline of the numbers. Two sampling method are provided such as ‘Latin-Hypercube’ and ‘Random sampling’. ‘Latin-Hypercube’ is recommended. It is noted that ‘Get From Simulation History’ can be included to the new sample points.
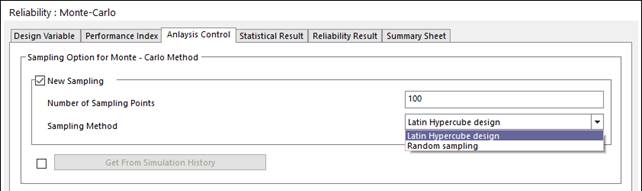
Figure 4 Define the Analysis Control