
1. Select the DFSS/Robust icon of the Optimization group in the AutoDesign tab.

Figure 1 DFSS/Robust icon of the Optimization group in the AutoDesign tab
2. Define design variables with statistical information
Check design variables in the ‘Design Variable’ page of the ‘DFSS/Robust Design Optimization’ dialogue and define statistical information of design variables.
•Variable Type: Design variable is defined and changed as a value between lower and upper bound during AutoDesign process. For the DFSS/Robust design optimization, it can be defined as random or deterministic variable. Standard deviation[SD] or coefficient of variation[COV] is defined to the random design variables. For the detailed information, one may refer to “Random Variables” in Guideline
•Constant Type: Design variable is defined as a constant value. But the statistical definition is applied the constant type design variables like as variable types. For the detailed information for the usage of constant type, one may refer to “Random Constants” in Guideline.
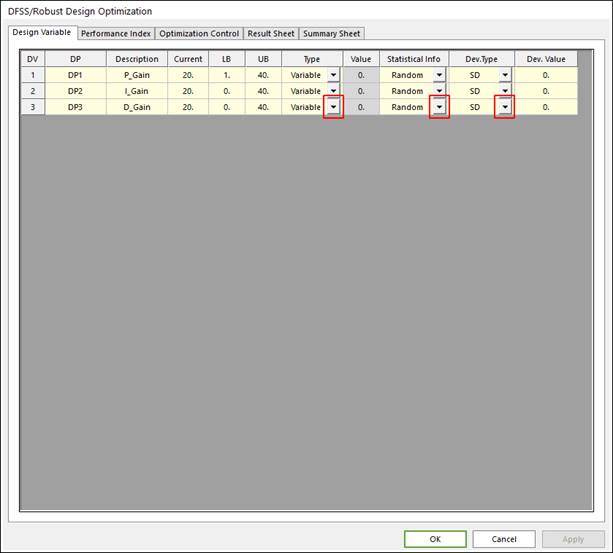
Figure 2 Design Variables tab of the DFSS/Robust Design Optimization dialog box
3. Formulate design optimization problem
The same step as the design optimization problem is applied to formulate ‘DFSS/Robust design optimizations’. Added index and weight values for DFSS/robust design are applied on each performance index. Refer to the Robust Design Optimization and Design For Six-Sigma(DFSS).
•Objective function: Select definition type as ‘Objective’, and goal type as ‘Min’ or ‘Max’. Next, define the weight value in ‘Weight/Limit Value’ section. And define the robust index and Alpha weight.
•Constraint condition: Select definition type as ‘Constraint’, and goal type as ‘LE’ or ‘GE’ or ‘EQ’. Next, define the limit value in ‘Weight/Limit Value’ section. For the case of inequality constraint, the robust index is applied on the defined performance index.
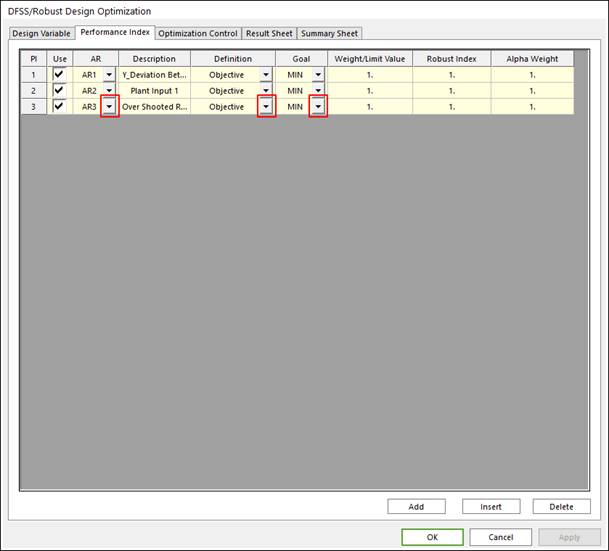
Figure 3 Performance Index tab of the DFSS/Robust Design Optimization dialog box
4. Select DOE and Meta modeling method, and polynomial function type.
This step is same in the case of design optimization problem.
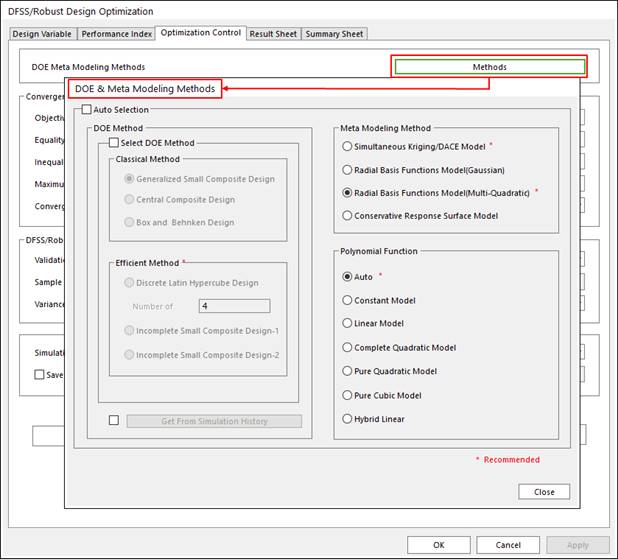
Figure 4 Select Method Options
5. Run optimization
Define convergence tolerance, DFSS/Robust design control and run robust design optimization. The run process is same as the case of design study process.
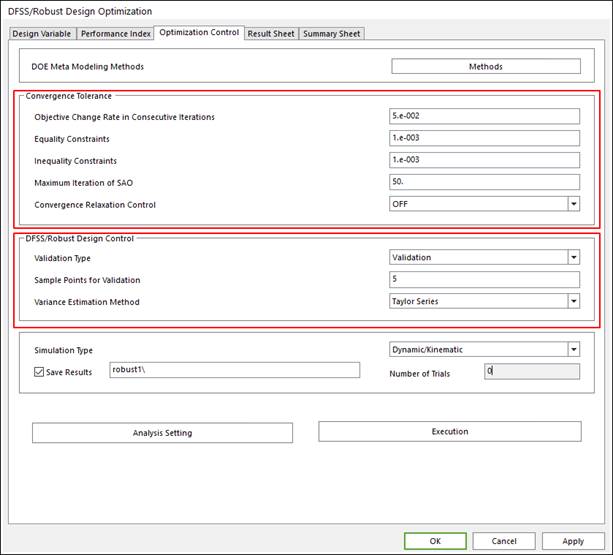
Figure 5 Optimization Control Dialog box
•Convergence Tolerance: The definition is same as the case of design optimization. The guide for defining the convergence tolerance is in the Guide for Convergence Tolerance.
•DFSS/Robust Design Control: Select the validation type as ‘None’, ‘Validation’, and ‘Validation & Re-Optimization’. ‘None’ don’t need ‘Sample Points for Validation’ definition. The guide for defining DFSS/Robust Design Control is explained in Validation of Robust Design and DFSS of Guideline.