All elements have an associated property of the appropriate material type.
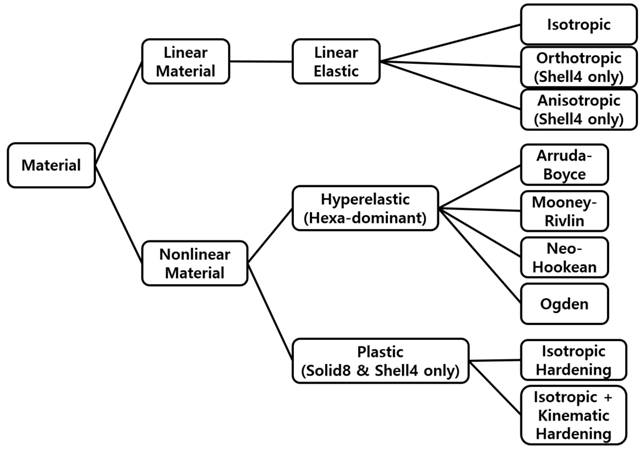
•Isotropic Materials:
•Has the same quality on direction
•Is used universally
•Orthotropic Materials:
•Has different quality about two orthogonal directions of shell plane
•Is used to paper, film etc.
•Anisotropic Materials:
•User-defined 3x3 matrix is used for constitutive equation
•Is used to materials which have different properties in different directions.
•Hyperelastic Materials:
•Rubber or rubber-like materials
•Initially isotropic
•Nonlinear
•Uses a large strain measure
•All strain energy is recoverable
•Plastic Materials:
•J2 (von Mises) plasticity material formulation
•Rate independent plasticity
•Appropriate for metal plasticity
The outline diagram of material is as fallowing figure.

Figure 1 Diagram of material of FFlex body
Figure 2 Material icon of the FFlex Edit group in the FFlex Edit tab
Step to create an FE material
1. Click the Material icon of the FFlex Edit group in the FFlex Edit tab.
2. The dialog box for the material list appears.
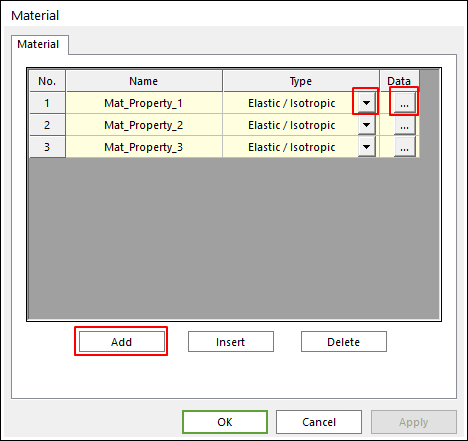
Figure 3 Material dialog box
3. Click Add.
4. Click  and then select the material type.
and then select the material type.
5. Click  of the newly created line.
of the newly created line.
Supported Material type
Some kinds of material types are supported for Shell/Solid element. Refer to Table 1.
|
Element Type |
Elastic |
Hyperelastic |
Rubber |
Plastic | |
|
1D element |
Beam 2 |
O |
X |
X |
X |
|
2D element |
Shell 3 |
O |
X |
X |
X |
|
Shell 4 |
O |
X |
X |
O | |
|
Shell 9 |
O |
X |
X |
X | |
|
3D element |
Solid 4 |
O |
O |
O |
O |
|
Solid 5 |
O |
O |
O |
O | |
|
Solid 6 |
O |
O |
O |
O | |
|
Solid 8 |
O |
O |
O |
O | |
|
Solid 10 |
O |
X |
X |
X | |
|
Solid 26 |
O |
X |
X |
X | |
Table 1 Supported material type.