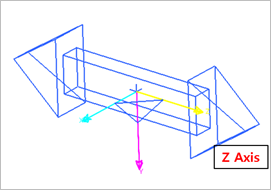
A translational joint allows one part to translate along a vector in respect of another part. The parts can only translate, not rotate, in respect of each other. This joint has one translational degree of freedom, and the rotational degree of freedom is 0. An axis of the translation is the z-axis. When the user creates a translational joint, the user specifies its location and orientation. The location of a translational joint does not affect the motion of the joint. The orientation of the translational joint, however, decides the direction of the axis along which the parts can slide in respect of each other. The direction of the motion of the translational joint is parallel to the orientation vector and passes through the location.

Figure 1 Translational Joint icon on Working Window
Figure 2 Translate icon of the Joint group in the Professional tab