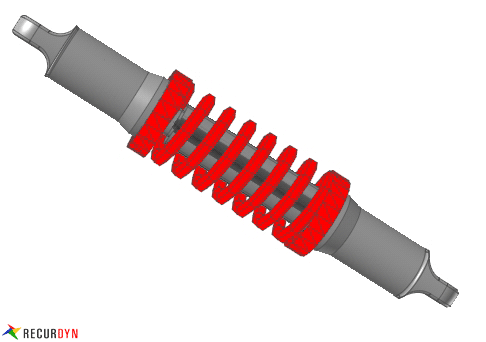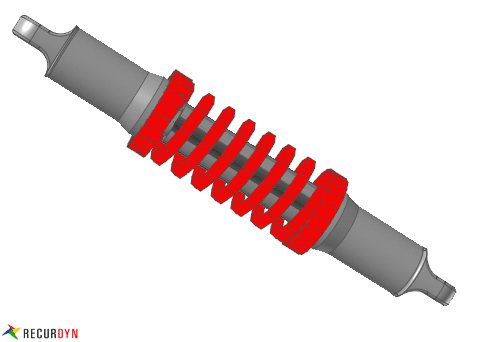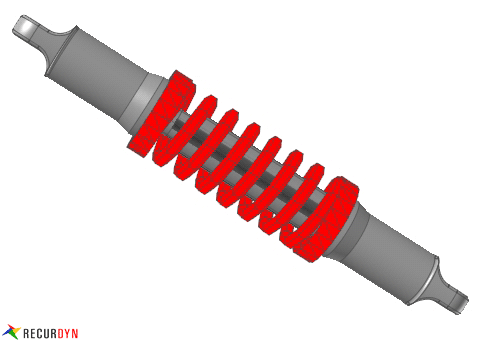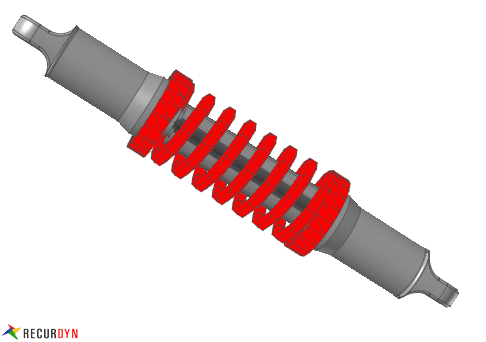

Figure 1 Spring example
RecurDyn/Spring has four kinds of MMS springs, which are MMS type A, MMS type B, MMS type C and MMS type D.
•The MMS Type A is composed of multi-mass bodies, which are connected with translational joints, TSDAs (translational spring damper) and axial force. The axial force is used to define coil clash using Impact function.
•The MMS Type B is a method for modeling the multi-mass-spring and this method is supplied by BMW AG. MMS Type B is composed of geometric spring shape and multi-mass bodies, which are connected with translational joints and axial force. The axial force represents nonlinear spring characteristic using interpolation of stiffness/damping splines.
•The MMS Type C is composed of a geometric spring shape and Multi Mass bodies (spheres), which are connected with translational joints and axial force. The axial force represents nonlinear stiffness characteristics between Multi Mass Bodies. There are two types of spring, which are One-Step and Two Step. They are different in the nonlinear character.
•The MMS Type D, 3D Multi Mass Spring is composed of a geometric spring shape and Multi Mass bodies, which are connected with beam forces, and contact forces for modeling contact situation. The beam force, which is defined by beam properties (Young’s modulus, shear modulus, cross section area, etc.), represents nonlinear stiffness characteristics between Multi Mass Bodies. Two kinds of contact force can be defined for MMS Type D. The one is for the contact situation between up and down helix of the spring. The other is for the contact situation between two MMS type Ds.
Figure 2 Spring group in the Toolkit tab