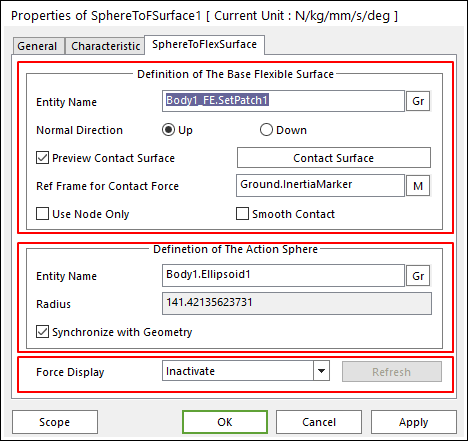

Figure 1 Properties of SphereToFSurface dialog box
•Definition of The Base Surface: Allows you to select the base contact geometry. The entities vary according to each contact force type.
•Definition of The Action Surface: Allows you to select the action contact geometry. The entities vary according to each contact force type.
•Force Display: Graphically displays the resultant force vector on the view window.
•Inactive: The force graphical display is inactive.
•Action: The force and torque which is generalized on the action body due to a contact force is displayed at a position. If the action body is a:
o Flexible body, then the resultant contact force is displayed at the specified reference frame for contact.
o Rigid body, then the contact force is displayed at the center marker of the action body.
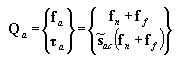
•Base: The force and torque which is generalized on the base body due to a contact force is displayed at a position. If the base body is a:
o Flexible body, then the resultant contact force is displayed at the specified reference frame for contact.
o Rigid body, then the contact force is displayed at the center marker of the base body.
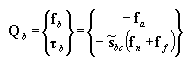
•Both: Simultaneously displays the action and reaction forces at the specified positions.
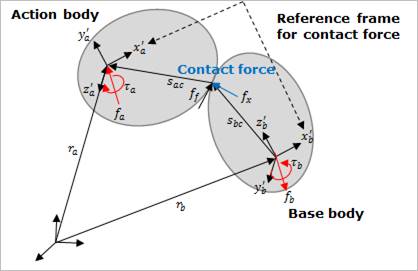
Figure 2 Definition of contact force
•Refresh: When the action or base contact geometry is changed, you can refresh the preview of information of specified contact geometry as using this function.
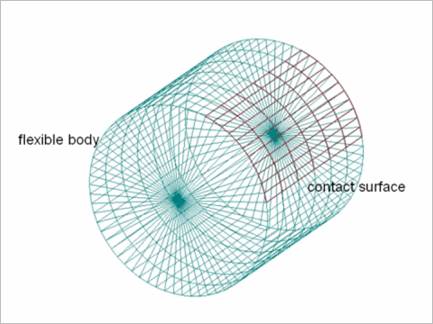
Figure 3 contact surface
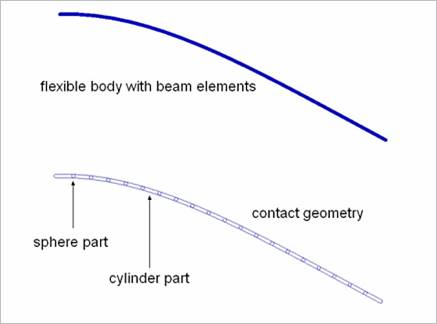
Figure 4 Contact curve
A FFlex body such as a cable or wire, or a beam structure with circular cross section is used for a contact.
•These Flexible bodies:
•Have a cylindrical surface.
•Is modeled with 1D finite element of beam.
•The beam elements is:
•Defined as a patch set
•Used for flexible curve contacts.
•The cross section of the curve for a contact is assumed as a circle.
•So, the contact geometry can be approximated to the cylinder and sphere as shown in Figure 2.
•Note that a contact point in the curve is linearly interpolated from two nodes.