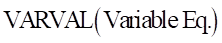
The VARVAL function returns the result of a variable equation and enables an expression to use the calculation derived from a variable equation entity.
Format
Arguments definition
|
Variable Eq. |
The name or argument number for the variable equation entity |
Example
VARVAL(Model1.DE1)
VARVAL(1) <Argument: (1)DE1>
1. Create two expressions for Variable Equation.
•Test1: sin(2*pi*time)
•Test2: 2*sin(2*pi*time*0.5)

2. Create two variable equations.
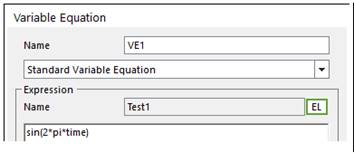
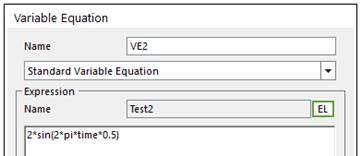
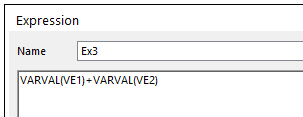
3. Create an expression for VE1 add VE2.
•Ex3: VARVAL(VE1) + VARVAL(VE2)
4. Make an expression scope.
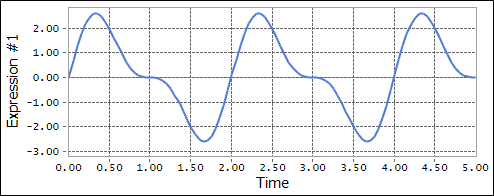
Figure 1 Scope result using the VARVAL function