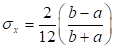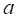 and
and
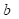 .
.
Sometimes, there is not enough information available to
determine the use of a particular standard distribution. From the empirical
experience, one can have some guideline of the lower and upper bounds of a
random variable, but there may not be enough data available between these two
bounds to justify a specific distribution. In this situation, a uniform
distribution is widely used even though any distribution can be used such as
triangular, trapezoidal and uniform, etc. Figure 1 shows a uniform distribution
with two limits 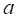 and
and
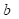 .
.
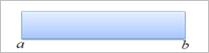
Figure 1 Uniform distribution
Then, the mean and the coefficient of variance are specified as
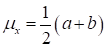 and
and