Contact problems
•If a contact between a track link assembly and the other Track (LM) entity (a flange or a sprocket) does not work.
•Contact search algorithm of a flange or a sprocket changes from the partial search to the full search.
•When the user wants to use the Geo Contact
•The action body of the Geo Contact must be the converted link body or the flexible link body.
When the small step-size error occurred using a flexible link body.
When a bushing force connected to the flexible link body is too big, the small step-size error occurs. Usually, the pin gap of a link assembly is not zero. It means the bushing force has an initial force. (The difference of between the action and base marker generates a force and a torque.)
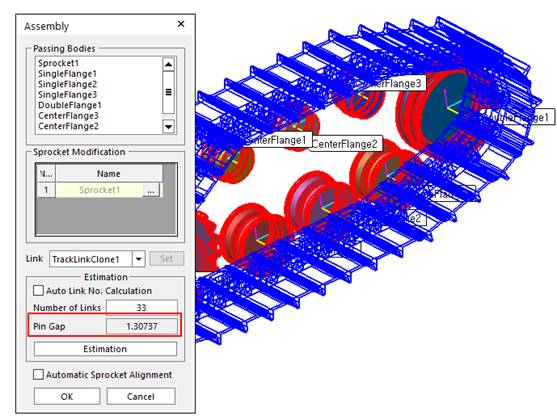
1. Assembly links.
① The distance between the pin and the hole in the adjacent two links named “Pin gap” must have a small value. The pin gap directly influences to the distance of between the action and base markers to the bushing force. Figure1 shows the pin gap when the user makes a track link assembly.

Figure 1 Pin gap
② When selecting a target link which will be converted to a flexible body, select a link has a small pin-gap between the target link and the adjacent link. Figure2 shows that a link of located in the circumference of a sprocket (or a flange) has a big pin-gap than the others.
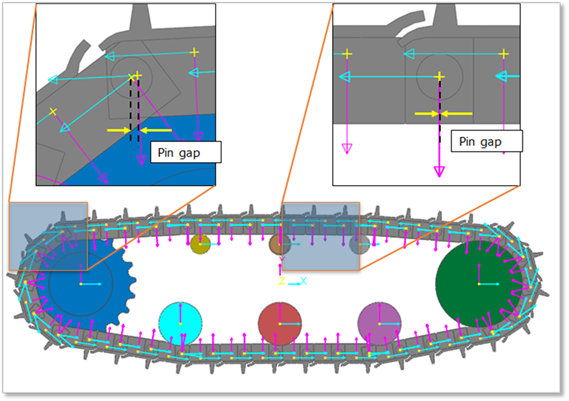
Figure 2 Selecting a target body to changing a flexible body
2. Modify bushing parameters
•Changes the stiffness of the bushing force connecting with a flexible body to a smaller value than the pin bushing.
•Note: This method influences that the pin-gap between the flexible link and an adjacent link will be increased as the simulation progressed.
3. Re-define the action and base markers of the bushing force
•Re-defines the action and the base marker of the bushing force connecting with the flexible link body to the same location.