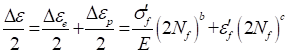
The strain life criterion is typically used for the low cycle fatigue; for example, the material fatigue due to the thermal cycle of structure. The stress level is higher and the number of cycles to failure may be lower.
Manson-Coffin Strain Life
The Manson-Coffin strain life equation can be written as
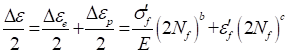
where
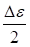 ∶ Normal strain amplitude for a
cycle
∶ Normal strain amplitude for a
cycle
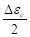 ∶ Normal elastic strain
amplitude for a cycle
∶ Normal elastic strain
amplitude for a cycle
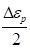 ∶ Normal plastic strain
amplitude for a cycle
∶ Normal plastic strain
amplitude for a cycle
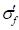 ∶ Fatigue strength
coefficient
∶ Fatigue strength
coefficient
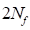 ∶ Reversals to failure
∶ Reversals to failure
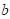 ∶ Fatigue strength exponent
(material property)
∶ Fatigue strength exponent
(material property)
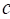 ∶ Fatigue ductility exponent
(material property)
∶ Fatigue ductility exponent
(material property)
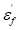 ∶ Fatigue ductility
coefficient
∶ Fatigue ductility
coefficient
In this life equation, only the strain amplitude is taken into account.
Morrow Strain Life
The Morrow strain life equation is shown below.
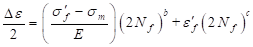
where
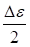 ∶ Normal strain amplitude for a
cycle
∶ Normal strain amplitude for a
cycle
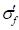 ∶ Fatigue strength
coefficient
∶ Fatigue strength
coefficient
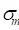 ∶ Mean stress for a cycle
∶ Mean stress for a cycle
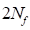 ∶ Reversals to failure
∶ Reversals to failure
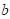 ∶ Fatigue strength exponent
(material property)
∶ Fatigue strength exponent
(material property)
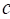 ∶ Fatigue ductility exponent
(material property)
∶ Fatigue ductility exponent
(material property)
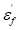 ∶ Fatigue ductility
coefficient
∶ Fatigue ductility
coefficient
The Morrow strain life criterion is also used for the low cycle fatigue. Besides the strain amplitude, the mean stress effect is also included in this life equation.
Smith-Watson-Topper (S-W-T)
The Smith-Watson-Topper (S-W-T) is typically used for low cycle fatigue. The S-W-T life equation of S-N Curve is shown below.
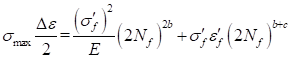
where
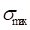 ∶ Maximum normal stress for a
cycle
∶ Maximum normal stress for a
cycle
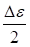 ∶ Normal strain amplitude for a
cycle
∶ Normal strain amplitude for a
cycle
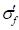 ∶ Fatigue strength
coefficient
∶ Fatigue strength
coefficient
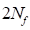 ∶ Reversals to failure
∶ Reversals to failure
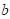 ∶ Fatigue strength exponent
(material property)
∶ Fatigue strength exponent
(material property)
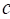 ∶ Fatigue ductility exponent
(material property)
∶ Fatigue ductility exponent
(material property)
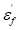 ∶ Fatigue ductility
coefficient
∶ Fatigue ductility
coefficient
Maximum Shear Strain
The maximum shear strain life approach is based on the assumption that the notch shearing strain amplitude will correlate the life with the shear strain amplitude in the uniaxial test specimens. It uses the shear strain amplitude on the maximum shear plane for the life equation as following:
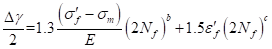
where
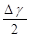 ∶ the shear strain amplitude
for a cycle
∶ the shear strain amplitude
for a cycle
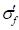 ∶ Fatigue strength
coefficient
∶ Fatigue strength
coefficient
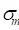 ∶ Mean stress for a cycle
∶ Mean stress for a cycle
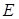 ∶ Elastic modulus (Young’s
Modulus)
∶ Elastic modulus (Young’s
Modulus)
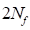 ∶ Reversals to failure
∶ Reversals to failure
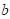 ∶ Fatigue strength exponent
(material property)
∶ Fatigue strength exponent
(material property)
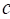 ∶ Fatigue ductility exponent
(material property)
∶ Fatigue ductility exponent
(material property)
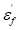 ∶ Fatigue ductility
coefficient
∶ Fatigue ductility
coefficient