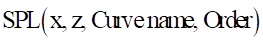
The SPL function uses the selected interpolation type in the spline curve. The spline curve function returns the y values for the x variable input through the spline entity. It uses spline curve in x-y direction and linear interpolate in x-z direction. So, if the user wants to smooth surface effect then data set of z direction must be dense.
Format
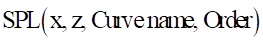
Arguments definition
|
|
An input variable for the spline function •Generally, this variable is time or a function that returns a real number. |
|
|
An input variable for the spline function •The second variable is necessary for three-dimensional spline functions. •This variable must be a function that returns a real number. Otherwise, 0 is applied. y1=f(x,z1), y2=f(x,z2) z1<z<z2 y = (z - z1) * (y2 – y1)/ (z2-z1) + y1 |
|
Curve name |
The name or argument number of the spline data defined by the subentity |
|
Order |
The interpolation method for the functions (return the value if 0, return calculation for 1st order differential equation if 1, and return calculation for 2nd order differential equation if 2) dy1/dx = df(x,z1)/dx, dy2/dx = df(x,z2)/dx dy/dx = (z - z1) * (dy2/dx – dy1/dx)/ (z2-z1) + dy1/dx |
Formulation
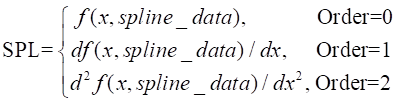
Example
SPL(time-4,0,1,0) <Argument: (1) Spline>
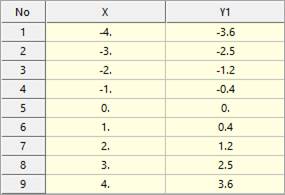
Figure 1 Spline Data
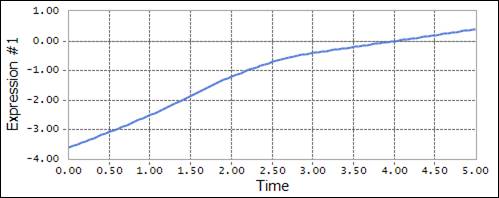
Figure 2 Example using the SPL function, selected interpolation type is Akima
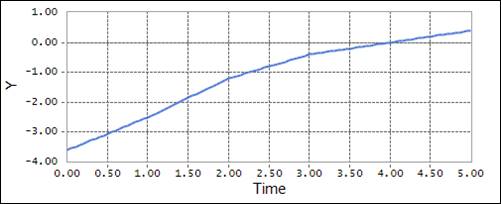
Figure 3 Example using the SPL function, selected interpolation type is Linear