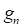 ) should be
less than that of the linear limit state function (
) should be
less than that of the linear limit state function (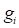 ). In Figure 1, the shade areas are the
failure regions, respectively.
). In Figure 1, the shade areas are the
failure regions, respectively.
When FORM applies to the limit state functions with
same MPP, their failure probabilities are estimated as equal values.
Figure 1 shows the linear and the nonlinear limit state functions with same
MPP. But it is apparent that the failure probability of nonlinear limit
state function(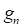 ) should be
less than that of the linear limit state function (
) should be
less than that of the linear limit state function (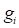 ). In Figure 1, the shade areas are the
failure regions, respectively.
). In Figure 1, the shade areas are the
failure regions, respectively.
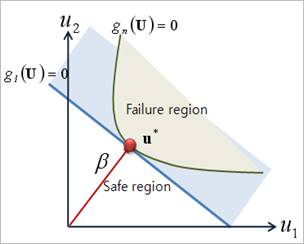
Figure 1 Linear and Nonlinear Limit State with sample MPP
The curvature of the nonlinear limit state function is ignored in the FORM approach, which uses only a first-order approximation at MPFP. Thus, the second-order reliability method (SORM) was widely studied to include the curvature information. The SORM analysis requires a second-order polynomial:
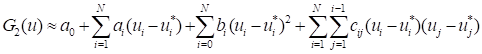
This definition requires 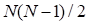 second order derivatives.
Breitung derived the following asymptotic formula for large
second order derivatives.
Breitung derived the following asymptotic formula for large
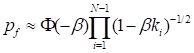
where 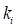 are the principal curvatures at the
most probable failure point. Although SORM could improve the accuracy, it
may become expensive if a large number of costly numerical analyses, such as
large-scale CAE analyses embedded in the limit state functions, are
involved.
are the principal curvatures at the
most probable failure point. Although SORM could improve the accuracy, it
may become expensive if a large number of costly numerical analyses, such as
large-scale CAE analyses embedded in the limit state functions, are
involved.