1. Select the Optimization icon of the Optimization group in the AutoDesign tab.

Figure 1 Optimization icon of the Optimization group in the AutoDesign tab
2. Define design variables
Check design variables in ‘Design Variable’ tab of the ‘Design Optimization’ dialog and select design variable type and value. For the usage of design variable types, one may refer to Guides for Design Variables and Constants.
•Variable type: Design variable is defined and changed as a value between lower and upper bound during AutoDesign process
•Constant type: Design variable is defined as a constant value. Some case user wants to settle down a design variable as a constant value because of design constraints or change of design direction during Design process. For this case, the value section of list is active, and one can write the constant value of design variable.
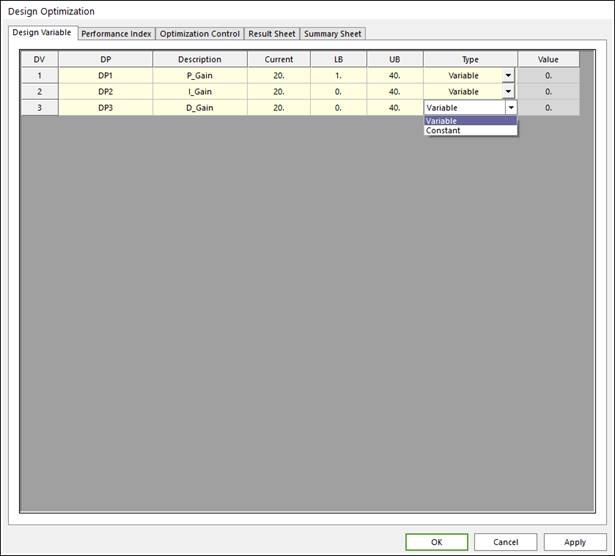
Figure 2 Design Variable tab of the Design Optimization dialog box
3. Formulate design optimization problem
First, Click the ‘Add’ button, and select an analysis response from full down list of ‘AR’ section. Next, select ‘Definition’ and the ‘Goal’ type and modify the ‘Weight/Limit Value’.
•Objective function: Select definition type as ‘Objective’, and goal type as ‘Min’ or ‘Max’. Next, define the weight value in ‘Weight/Limit Value’ section. For example, selecting ‘Min’ goal type and writing ‘10’ in ‘Weight/Limit Value’ section means minimization about that performance index with 10 weight value.
•Constraint condition: Select definition type as ‘Constraint’, and goal type as ‘LE’ or ‘GE’ or ‘EQ’. Next, define the limit value in ‘Weight/Limit Value’ section. For example, selecting ‘EQ’ goal type and writing ‘0.0’ in ‘Weight/Limit Value’ section means the constraint condition of that performance index is that the selected performance equals zero.
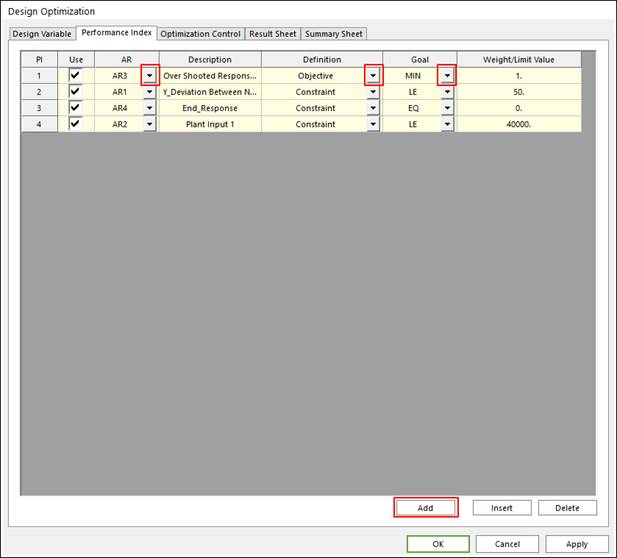
Figure 3 Performance Index tab of the Design Optimization dialog box
4. Select DOE and Meta modeling method, and polynomial function type.
The theoretical explanation of each DOE method and meta modeling technique is explained in Basic Theory. For the guideline for selecting DOE method, one may refer to Guides for the initial Sampling Method of Guideline.
•Number of Trials: This number is the summation the initial trial, which the current design variables are applied on, and the number of DOE trial. The number of DOE trial is automatically calculated from the selected DOE method.
•Get from simulation history: If one wants to use the result history data of former AutoDesign process, check the check box and click the ‘Get from History’ button. Then the simulation history dialogue is opened, and user can select the useful cases shown in Figure 5. The checked cases in the check box of ‘Import’ section is applied on the current process, but the selected case has the same number of design variable and performance indices as the current design problem.
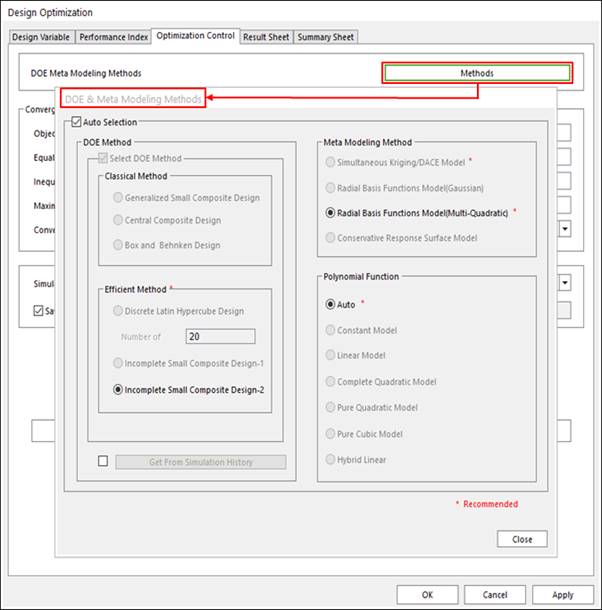
Figure 4 Select Method Options
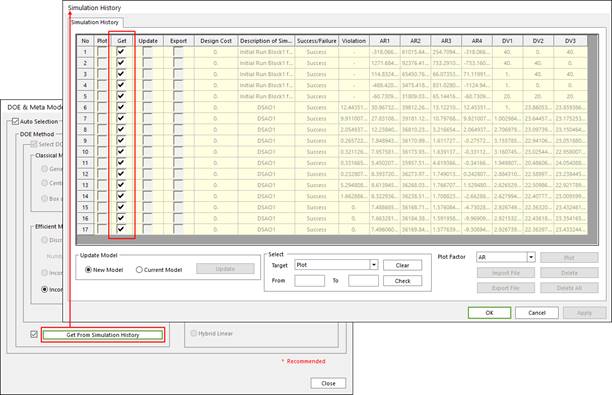
Figure 5 Select applied result in simulation history list
5. Run optimization
Define convergence tolerance and run optimization. The run process is same as the case of design study process.
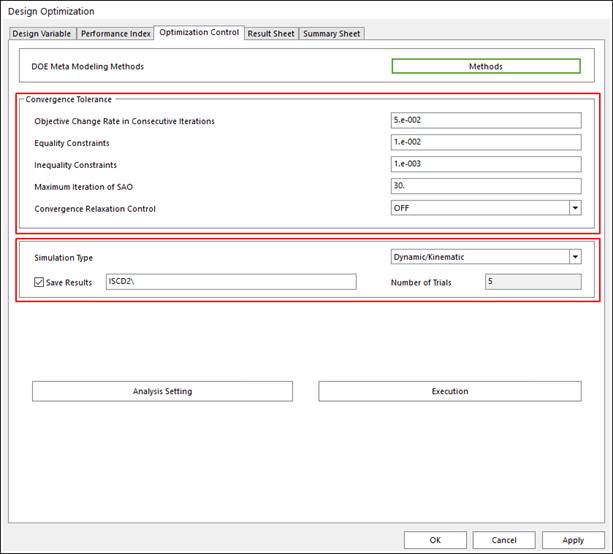
Figure 6 Optimization Control tab of the Design Optimization dialog box
•Convergence Tolerance: Each tolerance is defined convergence condition for objective function, equality and inequality constraint. The ‘Maximum Iteration of SAO’ can define the limit of trial in the SAO process. The guide for defining the convergence tolerance is explained in Guides for Convergence Tolerance.