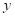 depends on the controllable
input variables
depends on the controllable
input variables 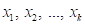 . The
relationship i
. The
relationship i
Response surface Method is an integration of
statistical and mathematical techniques useful for developing, improving, and
optimizing process. The most extensive applications of RSM are in the
industrial world, particularly in situations where several variables potentially
influence some performance measure or quality characteristics of the product or
process. In general, a product or system response 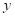 depends on the controllable
input variables
depends on the controllable
input variables 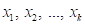 . The
relationship i
. The
relationship i
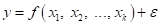
where the form of true response function 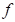 is unknown and perhaps very
complicated, and
is unknown and perhaps very
complicated, and 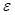 is a
term that represents other sources of variability not included in
is a
term that represents other sources of variability not included in 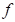 . In general, the statistical error
. In general, the statistical error 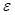 is a normal distribution
is a normal distribution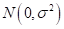 . Suppose that the response
surface models
. Suppose that the response
surface models 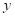 may be
represented by
may be
represented by
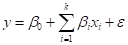 (Linear Model) and
(Linear Model) and
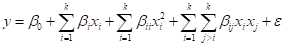 (Quadratic Model)
(Quadratic Model)
Where 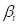 are the unknown coefficients. If
there is more than one data point under consideration, the linear model is
extended to the matrix form
are the unknown coefficients. If
there is more than one data point under consideration, the linear model is
extended to the matrix form
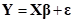
where 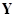 is a
vector of
is a
vector of 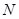 observations,
observations, 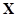 is a matrix of known
constant,
is a matrix of known
constant, 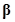 is a vector
of
is a vector
of 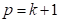 parameters, and
parameters, and 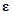 is the vector of random
errors. In order to obtain the unknown coefficients, we solve the sum of squares
of residuals as
is the vector of random
errors. In order to obtain the unknown coefficients, we solve the sum of squares
of residuals as 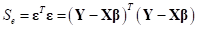 . To
minimize
. To
minimize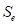 , we solve a set of
, we solve a set of
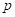 equations. Hence the normal
equation
equations. Hence the normal
equation 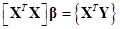 is obtained.
The matrix
is obtained.
The matrix 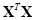 is a symmetric
matrix with
is a symmetric
matrix with 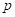 rows and
rows and
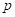 columns. Its rank is the same
as the rank of
columns. Its rank is the same
as the rank of 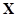 , which is the
number of linearly independent column of
, which is the
number of linearly independent column of 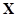 .
.
If the 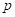 columns of
columns of 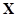 are linearly independent,
are linearly independent, 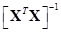 exists and the normal
equations have a unique set of solutions
exists and the normal
equations have a unique set of solutions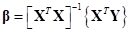 . However, if
. However, if 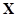 is less than full rank because the
columns are not linearly independent,
is less than full rank because the
columns are not linearly independent, 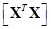 is singular and
is singular and 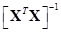 does not exist. It will, in fact, be
true of almost the experimental design models. Hence special numerical
techniques are required to construct the general response surface modeling
tools.
does not exist. It will, in fact, be
true of almost the experimental design models. Hence special numerical
techniques are required to construct the general response surface modeling
tools.