The MODAL FORCE EXT subroutine generates a user - defined RFlex Modal Force like FFLEX Nodal Force.
MODAL FORCE EXT is different with Modal force. It is not easy that the user want to make MODAL FORCE using USUB. Because of, there are so many argument.
However, MODALF FORCE EXT have same definition with NODAL FORCE EXT. If user want to make RFLEX MODAL FORCE, considering only NODAL FORCE.
The Recurdyn solver convert NODAL FORCE into MODAL FORCE.
|
Language type |
SubRoutine |
|
FORTRAN |
modal_force_ext (ID, TIME, UPAR, NPAR, IFBODY, NODARR, NONDE, JFLAG, IFLAG, RESULT) |
|
C/C++ |
modal_force_ext (int id, double time, double upar[], int npar, int ifbody, int nodarr[], int nonde, int jflag, int iflag, double result[]) |
Parameter information
|
Variable Name |
Size |
Description |
|
id |
int |
Modal Force sequential identification |
|
time |
double |
Current simulation time of RecurDyn/Solver. |
|
upar |
double* |
Parameters defined by the user. There is no limit about the maximum size of array. |
|
npar |
int |
Number of user parameters. |
|
ifbody |
int |
RFLEX body sequential identification defined in RecurDyn/Solver. |
|
nodarr |
int[nnode] |
Node ID array of input node set. |
|
nnode |
int |
Number of node of node set. |
|
jflag |
int |
When RecurDyn/Solver evaluates Jacobian, the flag is true. Otherwise, the flag is false. |
|
iflag |
int |
When RecurDyn/Solver makes its initial call to this routine, the flag is true. Otherwise, the flag is false. |
|
result |
double[nonde*6] |
Nodal forces. Acting point of the nodal force is each center of each node. Referece frame of each force vector must be the ground inertia marker |
Example

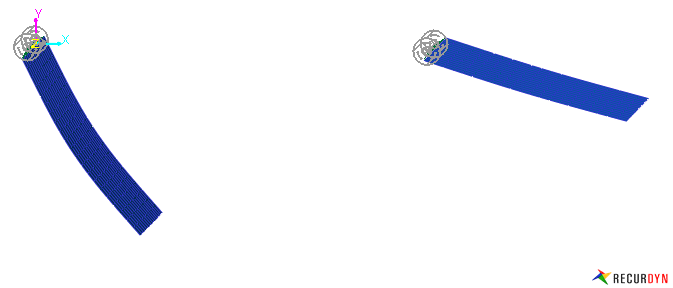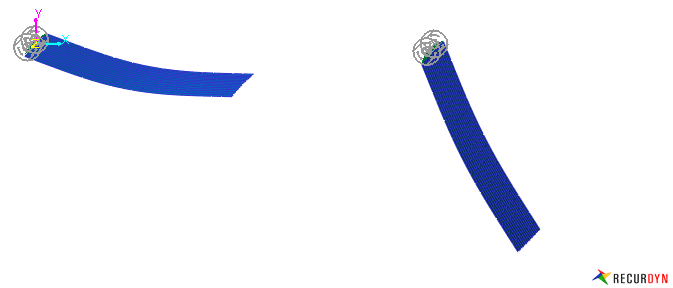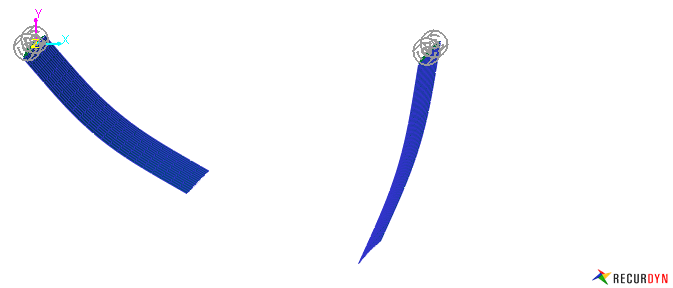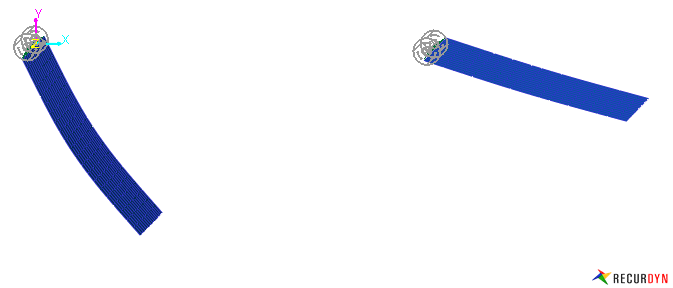
Figure 1 Modal force model applying air resistance effect using modal force ext USUB.