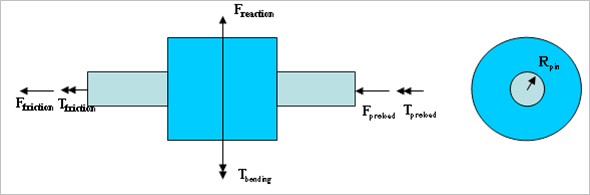
In case of the cylindrical joint, there is one friction type.
Sliding and Stiction Type Friction
A friction force which contains a sliding and stiction algorithm can be defined on the cylindrical joint. Include Friction option in Joint property page must be checked to use the friction force.

Figure 1 Configuration of Sliding and Stiction Friction Force on Cylindrical Joint
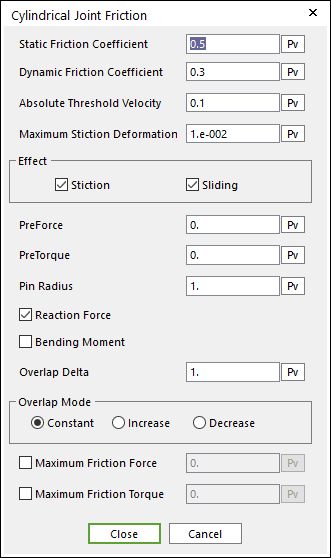
Figure 2 Cylindrical Joint Friction dialog box
The frictional force and torque are calculated according to the following equations:
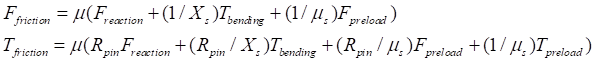
where,
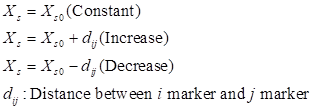
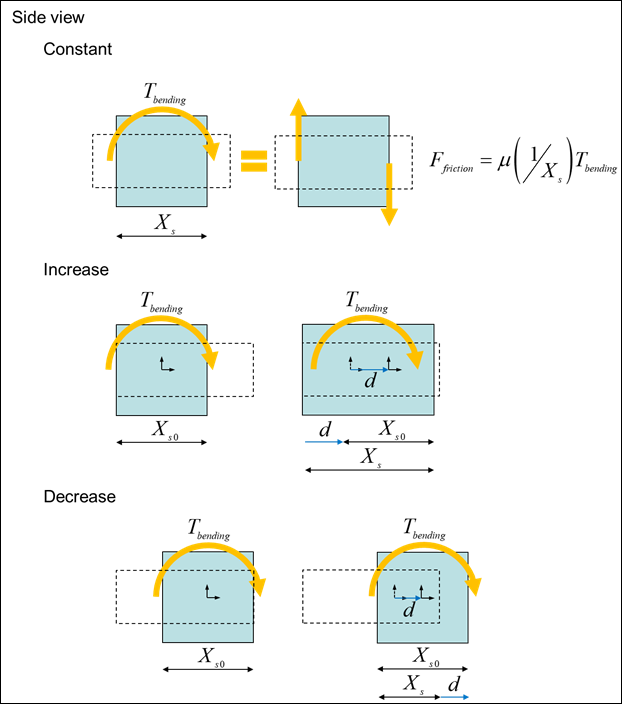
Figure 3 Detail of Overlap Mode and Delta
Where, the inputs into the equation are defined in the following table:
|
Current Friction Coefficient |
|
The coefficient of friction calculated during the simulation is a function of the relative velocity between body surfaces. |
|
Static Friction Coefficient |
|
The coefficient of friction is zero at a zero velocity,
but it smoothly transitions to the static coefficient of friction at
Absolute Threshold Velocity ( |
|
Effect |
|
Checks Stiction or Sliding.
For more information, click here. |
|
PreForce |
|
A constant frictional force that acts during the entire simulation. |
|
PreTorque |
|
A constant frictional torque that acts during the entire simulation. |
|
Pin Radius |
|
The radius of the smaller surface geometry in the revolute joint. |
|
Reaction Force |
|
The force in the joint calculated during the simulation in the direction along the rotational axis. |
|
Bending Moment |
|
The calculated torque that acts at right angles to the rotational axis. |
|
Overlap Delta |
|
A distance that starts at a nominal value and increases according to the translation of the action body with respect to the base body. |
|
Overlap Mode |
|
Selects Constant, Increase, or Decrease. |
|
Maximum Friction Force |
|
Collisions during contact as well as transitions during sliding forces can result in force spikes. High frictional forces can result from these spikes. This option allows a maximum friction force to be defined that should correspond to the maximum expected steady-state force. |
|
Maximum Friction Torque |
|
Collisions during contact as well as transitions during sliding forces can result in force spikes. High frictional torques can result from these spikes. This option allows a maximum friction torque to be defined that should correspond to the maximum expected steady-state force. |