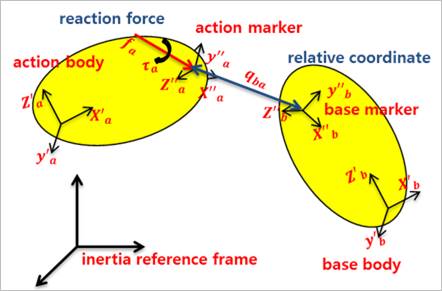
The lists of Joints include a result set about each joint. Especially, some joints report their relative coordinates, velocities and accelerations.

Figure 1 Definition of joint plot data
•Pos_Relative: The relative coordinates as shown in Table 1.
|
Joint |
Index |
Definition |
|
Revolute |
Pos1 |
The rotational angle of the z-axis of the action marker with respect to the z-axis of base marker. |
|
Translational |
Pos1 |
The translational displacement of the action marker relative to the base marker along the z-axis of base marker. |
|
Spherical |
Pos1 |
The Psi angle when the orientation of action marker with respect to the base marker is expressed in the Euler Psi - Theta -Phi angle. |
|
Pos2 |
The Theta angle when the orientation of action marker with respect to the base marker is expressed in the Euler Psi - Theta-Phi angle. | |
|
Pos3 |
The Phi angle when the orientation of action marker with respect to the base marker is expressed in the Euler Psi - Theta -Phi angle. | |
|
Cylindrical |
Pos1 |
The translational displacement of action marker relative to the base marker along the z-axis of base marker. |
|
Pos2 |
The rotational angle of the z-axis of action marker with respect to the z-axis of base marker. | |
|
Universal |
Pos1 |
The rotational angle of the x-axis of action marker with respect to the z-axis of base marker. |
|
Pos2 |
The rotational angle of the x-axis of base marker with respect to the z-axis of action marker. | |
|
Planar |
Pos1 |
The translational displacement of action marker relative to the base marker along the x-axis of base marker. |
|
Pos2 |
The translational displacement of action marker relative to the base marker along the y-axis of base marker. | |
|
Pos3 |
The rotational angle of the z-axis of action marker with respect to the z-axis of base marker. | |
|
Screw |
Pos1 |
The relative displacement from the base marker to the action marker in the z-axis of base marker. |
|
Atpoint
|
Pos1 |
The Psi angle when the orientation of action marker with respect to the base marker is expressed in the Euler Psi - Theta -Phi angle. |
|
Pos2 |
The Theta angle when the orientation of action marker with respect to the base marker is expressed in the Euler Psi - Theta -Phi angle. | |
|
Pos3 |
The Phi angle when the orientation of action marker with respect to the base marker is expressed in the Euler Psi - Theta -Phi angle. |
Table 1 Definition of relative coordinates
•Vel_Relative: The relative velocities as shown in Table 2.
•Acc_Relative: The relative accelerations as shown in Table 2.
|
Joint |
Index |
Definition |
|
Revolute |
Vel1 Acc1 |
The rotational velocity and acceleration of the z-axis of action marker with respect to the z-axis of base marker. |
|
Translational |
Vel1 Acc1 |
The translational velocity and the acceleration of action marker relative to the base marker along the z-axis of base marker. |
|
Spherical |
Vel1 Acc1 |
The x component of the rotational velocity and the acceleration of action marker relative to the base marker in the base marker reference frame. |
|
Vel2 Acc2 |
The y component of rotational velocity and the acceleration of action marker relative to the base marker in the base marker reference frame. | |
|
Vel3 Acc3 |
The z component of the rotational velocity and the acceleration of action marker relative to the base marker in the base marker reference frame. | |
|
Cylindrical |
Vel1 Acc1 |
The translational velocity and the acceleration of action marker relative to the base marker along the z-axis of base marker. |
|
Vel2 Acc3 |
The rotational velocity and the acceleration to the z-axis of action marker with respect to the z-axis of base marker. | |
|
Universal |
Vel1 Acc1 |
The z component of the rotational velocity and the acceleration of action marker relative to the base marker in the reference frame Vel2 of base marker. |
|
Vel2 Acc2 |
The z component of the rotational velocity and the acceleration of base marker relative to the action marker in the reference frame of action marker. | |
|
Planar |
Vel1 Acc1 |
The translational velocity and the acceleration of action marker relative to the base marker along the x-axis of base marker. |
|
Vel2 Acc2 |
The translational velocity and the acceleration of action marker relative to the base marker along the y-axis of base marker. | |
|
Vel3 Acc3 |
The rotational velocity and acceleration of the z-axis of action marker with respect to the z-axis of base marker | |
|
Screw |
Vel1 Acc1 |
The translational velocity and the acceleration of action marker relative to the base marker along the z-axis of base marker |
|
Atpoint |
Vel1 Acc1 |
The x component of the rotational velocity and the acceleration of action marker relative to base marker in the reference frame of base marker. |
|
Vel2 Acc2 |
The y component of the rotational velocity and the acceleration of action marker relative to the base marker in the reference frame of base marker. | |
|
Vel3 Acc3 |
The z component of the rotational velocity and the acceleration of action marker relative to the base marker in the reference frame of base marker. |
Table 2 Definition of relative velocities and accelerations
•FM_Reaction_Force: The magnitude of the translational force acting at the action marker.
•FX_Reaction_Force, FY_Reaction_Force, FZ_ Reaction_Force:
•PTCV, CVCV: The x, y, and z components of the translational force applied at the action contact point in the inertia reference frame.
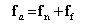
•The other joints: The x, y, and z components of the translational force acting at the action marker in the reference frame of base marker.
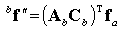
•TM_ Reaction_Force: The magnitude of the torque acting at the action marker.
•TX_ Reaction_Force, TY_ Reaction_Force, TZ_ Reaction_Force:
•PTCV, CVCV: The x, y, and z components of the rotational torque applied at the action contact point in the inertia reference frame. The values are always zero.
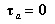
•The other joints: The x, y, and z components of the torque acting at the action marker in the reference frame of base marker.
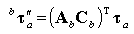
•Driving_Force/Torque: The driving force or torque generated by the only specified Motion of Revolute, Translational, Cylindrical, Spherical, and Universal Joints.
•Friction_Force/Torque: The friction force or torque generated by the specified Friction of Revolute and Translational Joints.
•Joint1_Driving_Force/Torque: The driving force or torque of Revolute and Translational Joints on which generated by the specified Gear.
•Joint2_Driving_Force/Torque: The driven force or torque of Revolute and Translational Joints on which generated by the specified Gear.
•Driver_Driving_Force/Torque: The driving force or torque of Revolute, Translational and Cylindrical Joints on which generated by the specified Coupler.
•Coupled_Driving_Force/Torque: The driven force or torque of Revolute, Translational and Cylindrical Joints on which generated by the specified Coupler.
Note: The driving force or torque applied on the joint should equal to the driving force and torque due to all couplers, gears and motions defined on the joint.
•DM_FloatBase: For PTCV and CVCV, the magnitude of translational displacement of the base contact point with respect to the reference frame of base body.
•DX_FloatBase, DY_FloatBase, DZ_FloatBase: For PTCV and CVCV, the x, y and z components of translational displacement of the base contact point with respect to the reference frame of base body.
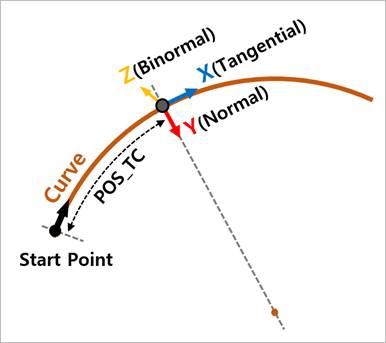
•POS_TC: For PTCV, the curved distance between start point of curve and action marker.
•Reaction_Force_Tangential: For PTCV, the translational force acting at the action marker in the tangent vector to a curve.
•Reaction_Force_Normal: For PTCV, the translational force acting at the action in the vector perpendicular to the tangent vector to a curve.
•Reaction_Force_Binormal: For PTCV the translational force acting at the action marker in the vector perpendicular to both the tangent and normal vectors to a curve.
•DM_FloatAction: For CVCV, the magnitude of translational displacement of the action contact point with respect to the reference frame of the action body.
•DX_FloatAction, DY_FloatAction, DZ_FloatAction: For CVCV, the x, y and z components of translational displacement of the action contact point with respect to the reference frame of action body.
•NF_Contact: For CVCV, the translational force acting at the action contact point in the vector perpendicular to the tangent vector to action curve.
•Base_Curve_Curvature: For CVCV, it becomes the curvature of base curve on the curve point.
For a space curve given parametrically in Cartesian coordinates by f(u) = (x(u), y(u), z(u)), the curvature is
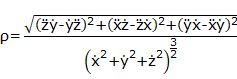
where the dot denotes differentiation with respect to the parameter u.
•Action_Curve_Curvature: For CVCV, it becomes the curvature of action curve on the curve point.