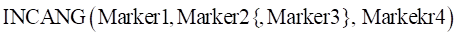
The INCANG function returns the angle in radians between 2 vectors that are made from the positions of either 3 or 4 markers. If the vectors continue to rotate in the same direction past 180 degrees, then the angle returned increases beyond 180 degrees.
(Note: The initial value of INCANG is between 0 and 180, inclusive)
Format
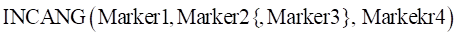
Arguments definition
|
Marker1 |
The name or argument number of a marker to be calculated. (the end point of the 1st vector) |
|
Marker2 |
The name or argument number of a marker to be calculated. (the start point of the 1st vector) |
|
Marker3 |
The name or argument number of a marker to be calculated. (the start point of the 2nd vector) •If omitted, then the Marker2 is applied. |
|
Marker4 |
The name or argument number of a marker to be calculated. (the end point of the 2nd vector) |
Formulation
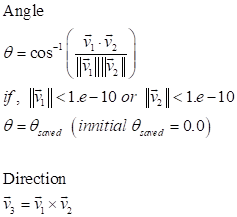
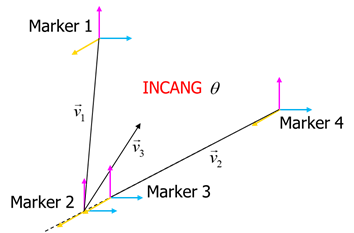
The first value of INCANG is positive angle and the value of INCANG is the cumulative angle on the simulation.
Example
INCANG (body1.Marker1, Ground.InertiaMarker, body2.Marker1)
INCANG (body1.Marker1, body1.Marker2, body2.Marker1, body2.Marker2)
INCANG (1,2,3) <Argument: (1)body1.Marker1, (2)Ground.InertiaMarker, (3)body2.Marker1 >
INCANG (1,2,2,3) <Argument: (1)body1.Marker1, (2)Ground.InertiaMarker, (2)Ground.InertiaMarker, (3)body2.Marker1 >