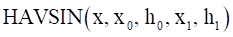
The HAVSIN function interpolates between two markers using a trigonometric function. Generally, this function is used to link two markers in a gradual curve, similar to the Step and Step 5 functions.
Format
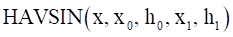

Arguments definition
|
|
The input variable for the defined HAVSIN •Generally, this variable is time or a function that returns a real number. |
|
|
The starting point for the HAVSIN function |
|
|
The initial value for the input variable (within the range of x≤x0) |
|
|
The ending point for the HAVSIN function |
|
|
The initial value for the input variable (within the range of x≥x1) |
Formulation
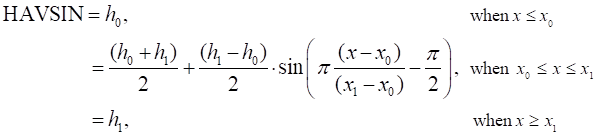
Example
HAVSIN (time, 1.0, 0.0, 4.0, 1.0)
•x = time: Independent variable
•x0 = 1.0: The x-value at which the HAVSIN function begins
•h0 = 0.0: Initial value of the HAVSIN function
•x1 = 4.0: The x-value at which the HAVSIN function ends
•h1 =1.0 : Final value of the HAVSIN function
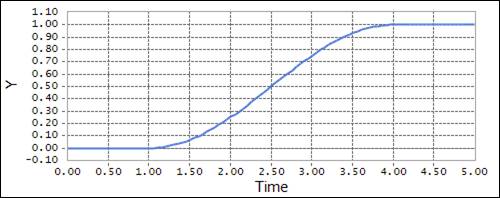
Figure 1 Scope result using the HAVSIN function