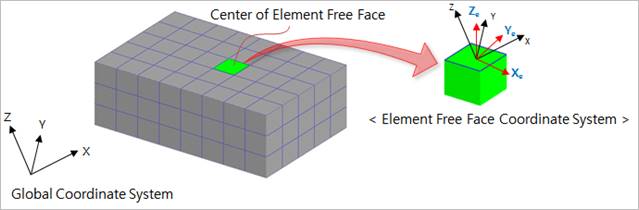
Theoretically, the fatigue analysis is to calculate the fatigue results such as Fatigue Damage, Fatigue Life and Safety Factor from a SN Curve through the selected fatigue material. In addition, physically, the initiation and propagation of the crack of structure takes place on the structure surface. Therefore, RecurDyn/Durability should focus the stress or strain results of element surface, Element Free Face. When calculating the fatigue results from FFlex or RFlex body, RecurDyn/Durability calculates by using the stress or strain results which are obtained after accomplishing the tensor transformation with respect to the center of Element Free Face from stress or strain results of elements as below.

Figure 1 Tensor transformation in center of Element Free Face
Maximum Damage Approach
In the maximum damage approach, the face reference frame of stress time history data w.r.t. is used. RecurDyn/Durability finds the highest damage and its direction on each element face. In other words, RecurDyn/Durability calculates the uniaxial or biaxial damage using the stress or strain history in different directions on element faces as shown in Figure 2. The directions to calculate damage on element face is defined increasing as incremental angle from X axis with respect to X-Y plane of element face coordinate system. And then, the highest damage will be used as the damage of element face and its direction will be treated as the effective loading direction.
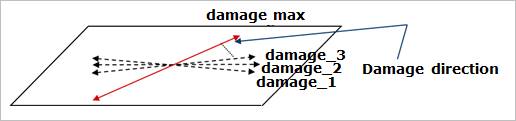
Figure 2 The concept of Maximum Damage Approach
Critical Plane Approach
In the critical plane approach, the part reference frame of strain time history w.r.t. is used. RecurDyn/Durability finds the maximum shearing (critical) plane and evaluates the stress/strain on the critical plane. This approach is best for the short stress/strain history data with very few cycles. In other words, RecurDyn/Durability calculates the uniaxial or biaxial damage using the stress or strain history in the principal directions on the maximum shearing (critical) plane determined by the maximum shear strain at the center of each element face.