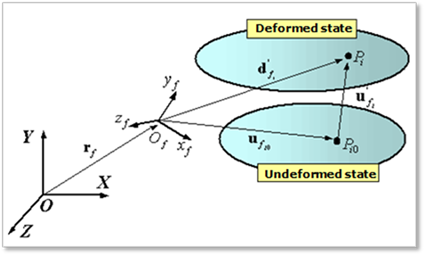

Figure 1 Configuration of a flexible body
Figure 1 shows the configuration of a flexible body f in the undeformed and deformed state. In the figure,
•XYZ : Inertia reference frame
•O : Origin of XYZ
•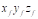 : Flexible body
reference frame
: Flexible body
reference frame
•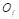 :Origin of
:Origin of 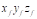
•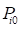 : Node i in the undeformed state
: Node i in the undeformed state
•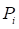 : Node i in the deformed state
: Node i in the deformed state
•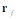 : Position vector from the point O to the point
: Position vector from the point O to the point 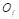
•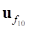 :
Position vector from the point
:
Position vector from the point 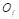 to the
to the 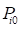
•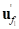 : Nodal elastic deformation position vector from the point
: Nodal elastic deformation position vector from the point 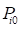 to the
to the 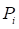 measured with respect to
measured with respect to 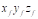 .
. 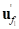 is nodal elastic deformation
is nodal elastic deformation
•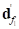 :
: 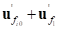 , position vector from the point
, position vector from the point
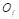 to the point
to the point 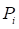
For a generic node 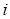 of a flexible body
of a flexible body 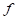 , position vector of the node can be
written as
, position vector of the node can be
written as
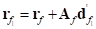 (1)
(1)
where,
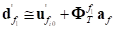 (2)
(2)
In above equation, 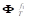 is the translational modal
matrix of a node
is the translational modal
matrix of a node 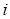 .
.
By taking time differentiation of the position vector,
velocity of the node 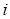 is obtained as follows;
is obtained as follows;
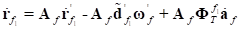 (3)
(3)
By taking time differentiation of the velocity vector,
acceleration of the node 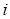 is obtained as follows;
is obtained as follows;
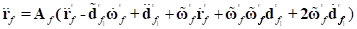 (4)
(4)
Where,
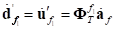 (5)
(5)
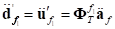 (6)
(6)
EOM
By the virtual work principle, equations of motion can be obtained as
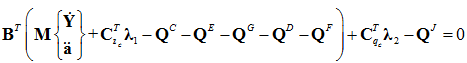
where,

