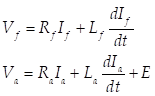
Electrical Part
The voltage equations of DC are as follows.
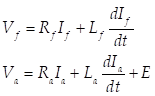
where, 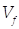 is the field voltage,
is the field voltage, 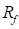 is the field resistance,
is the field resistance, 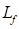 is the field inductance,
is the field inductance,
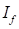 is the filed current,
is the filed current,
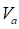 is the armature
voltage,
is the armature
voltage, 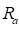 is the
armature resistance,
is the
armature resistance, 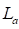 is
the armature inductance,
is
the armature inductance, 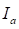 is the armature current, and E is the
back electromotive force.
is the armature current, and E is the
back electromotive force.
The field terminal and the armature terminal are separated so that the machine model can be a series-connected or a shunt-connected DC motors. A counter-electromotive force (CEMF), which is generated between the armature terminals, is proportional to the machine speed.
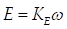
where, 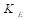 is the CEMF constant and
is the CEMF constant and 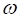 is the angular speed.
is the angular speed.
The CEMF constant 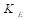 is proportional to the field current
is proportional to the field current
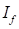
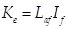
where, 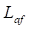 is the field-armature mutual
inductance.
is the field-armature mutual
inductance.
The torque, which is developed by DC motor, is proportional
to the armature current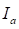 .
.
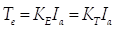
The torque constant 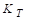 is equal to the CEMF constant
is equal to the CEMF constant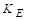 .
.
When the machine is in generator mode, the sign of torque is positive. In motor mode, the sign of torque is negative.
Mechanical Part
For more information, refer to PMDC Machine.