This page defines characteristic values to contact between two geometry entities. Geo Contact entities supported in RecurDyn are using this page.

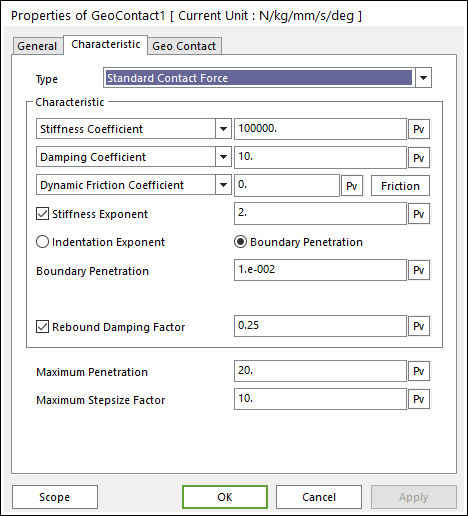
Figure 1 Geo Contact property page [Standard Contact Force]
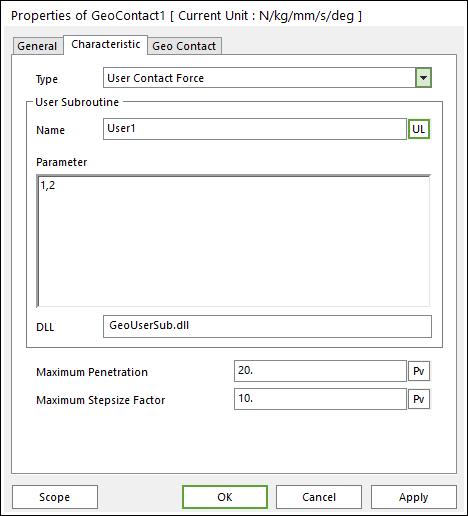
Figure 2 Geo Contact property page [User Contact Force]
•Type: Select a type as Standard Contact force or User Contact Force.
•Standard Contact Force: Defines the contact properties.
•User Contact Force: Defines by the user written contact subroutine (Refer Contact User Subroutine).
•Maximum Penetration: Specifies the maximum penetration depth. If the calculated penetration is larger than this value, the contact force in the given contact point will be ignored.
•Maximum Step Size Factor: The maximum step size is reduced by a factor of maximum step size factor.
Standard Contact Force
•Characteristic: Defines the contact properties such as the stiffness coefficient, damping coefficient, and friction coefficients. Also, these coefficients can be given as user-defined spline curves.
•Stiffness Coefficient: Specifies a stiffness coefficient for the contact normal force.
•Stiffness Spline: The spline shows the contact normal force for the penetration. For more information, refer to click here.
•Damping Coefficient: Specifies a viscous damping coefficient for the contact normal force.
•Damping Spline: The spline shows the contact normal force for the velocity of penetration. For more information, refer to click here.
•Dynamic Friction Coefficient: Specifies a dynamic friction coefficient for the contact friction force. It has three options.
o Dynamic Friction Coefficient: The constant friction coefficient is applied.
o Friction Force Spline: The spline shows the fiction force for the relative velocity. It is recommended to use the spline that x and y values are defined as positive.
o Friction Coefficient Spline: The spline shows the friction coefficient for the relative velocity.
•Friction: Specifies some friction coefficients for the contact friction force. The friction force calculation is same with the RecurDyn general contact characteristic page. Refer to Friction.
•Stiffness and Damping Exponent: Generates a non-linear contact normal force.
•Indentation Exponent: Yields an indentation damping effect. When the penetration is very small, the contact force may be negative due to a negative damping force, which is not realistic. This situation can be overcome by using the indentation exponent greater than one.
•Boundary Penetration: Specifies a full damping penetration. If the penetration is less than this value, the damping coefficient will be calculated with the STEP function. And if the penetration is equal or greater than this value, RecurDyn uses the user user–defined damping coefficient.
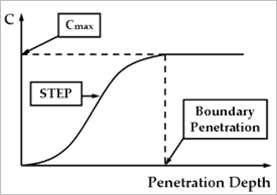
Figure 3 Damping Coefficient in the case of Boundary Penetration
•Rebound Damping Factor: To obtain realistic hysteric loop for energy dissipation during the contact, this rebound damping factor controls the rebound damping force when bodies are on restitution phase.
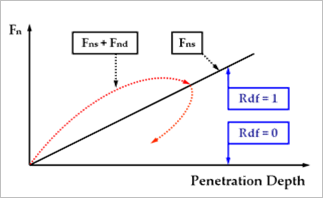
Figure 4 The hysteric loop and rebound damping factor
The contact normal force is calculated by
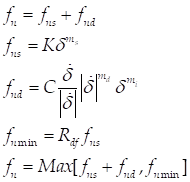
Where, K and C
are the spring and damping coefficients which are determined by an experimental
method, respectively. The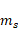
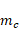
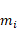
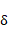
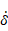
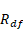
User Contact Force
•User Subroutine
•Name: Shows the name of user specified subroutine.
•Parameter: Shows the parameters used in the user specified subroutine.
•DLL: Shows the name of which DLL contains the Contact User Subroutine.